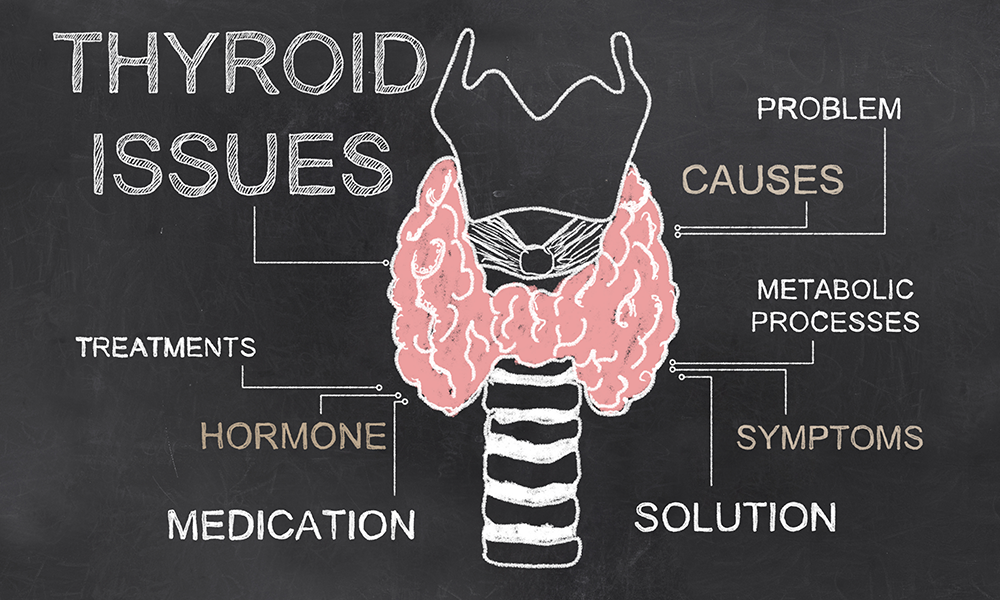
A butterfly-shaped gland, the thyroid is located just above the collarbone. It constitutes one of the endocrine glands which generates hormones responsible for controlling metabolism. Thyroid disorders can either rev up or slow down one’s metabolism since they disrupt production of hormones in the thyroid.
There is a wide range of symptoms that can be experienced when thyroid hormone levels are either too high or too low and one common symptom is hair loss.
There are several thyroid disorders that include;
- Goiter: this is when the thyroid gland enlarges.
- Thyroid nodules: presence of lumps in the thyroid gland
- Hyperthyroidism: when the thyroid gland generates more hormones that those required by the body
- Hypothyroidism: when the thyroid gland does not generate enough thyroid hormones
- Thyroiditis: swelling of the glands
In order to diagnose thyroid disease, a medical practitioner will first look at your medical history and then take a physical exam that includes thyroid tests. In some cases, a biopsy is used. Treatment of thyroid disorders mainly depends on the particular disorder and may either be through thyroid surgery, radioiodine therapy or medication.
Hair Loss due to Thyroid Disorders
Often, abnormal hormones are blamed for the loss of scalp hair but in reality they are the least cause for hair loss. There are different causes of hair loss and sometimes, its natural as one grows older to lose hair.
Prolonged and severe hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism can lead to hair loss on the entire scalp and not only discrete areas. Successful treatment of the disorder leads to recovery of hair although it may be incomplete. Hair recovery takes several months. Short-lived thyroid problems and mild hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism doesn’t lead to much hair loss.
There are thyroid disorders that come abruptly and are conspicuous and therefore can be diagnosed early while other conditions can be present for months or years before they are diagnosed. One experiences hair loss several months after they get thyroid disease since human beings have a long hair cycle. In some cases hair loss may follow treatment of the thyroid disorder and subsequent medication and one can erroneously blame the medication and withdraw treatment and this in turn will worsen hair loss.
Biotin
Biotin plays a vital role in preventing hair loss. A vitamin, it encourages hair growth. Deficiency of biotin leads to breakage of hair that results to hair loss.
Biotin and hair growth are directly related and therefore it is important that one incorporates biotin in their regular diet. Examples of foods that contain biotin include liver, egg yolk, brewer’s yeast, soybeans, oats, green peas, sunflower seeds, brown rice, bulgur, walnuts, cauliflower, avocado, legumes, mushrooms and fish.
However, biotin supplements are also recommended since it would take consumption of thousands of calories daily to reach the recommended level. Adding five to eight grams to your food twice everyday can go a long way in preventing hair loss.
Biotin is also referred to as Vitamin B7. Part of the Vitamin B complex, it is water-soluble. It is also worth noting that individuals with blood type A can’t absorb B vitamins. Persons with acid reflux and heartburn tend to absorb biotin slowly and as a result, hair loss may occur despite ingesting biotin.
It is common to find biotin in skin and hair beauty products. However, biotin is more beneficial when ingested than when applied to the skin.
There are several risk factors that can lead to biotin deficiency in the body and they include: excessive consumption of alcohol, pregnancy, smoking, prolonged use of antibiotic, consumption of copious amount of raw white eggs and serious digestive disorders like celiac disease and Crohn’s disease. Symptoms of biotin deficiency in the body can include hair loss, dry skin, muscle aches, digestive issues, cramps and mood changes.
Advantages of Biotin
- It is affordable
- Strengthens hair, nails and the skin
- Improves regulation of blood sugar
- Assists in weight loss
- Assists in processing of energy and transporting carbon dioxide out of the cells
Disadvantages of Biotin
- It can cause acne and skin breakouts
- May lead to allergic reactions when it interacts with some drugs
- Increases the risk of miscarrying in pregnant women
- High dosage may lead to stomach cramps and diarrhoea
- On ingestion, it may cause nausea
 Sudden Changes in Your Body
Sudden Changes in Your Body Temperature Tolerance Fluctuations
Temperature Tolerance Fluctuations Mental Sluggishness
Mental Sluggishness Hair and Skin Problems
Hair and Skin Problems